WhatsApp Cloud API Integration with Next.js - Part 1: Setup & Configuration
I'm not going to lie, integrating the WhatsApp Business Cloud API can be a journey. When I first tackled it, I felt like I was piecing together a puzzle with half the pieces missing. Meta's official documentation is spread across a dozen different pages, and finding a clear, start to finish guide for a modern stack like Next.js was nearly impossible.
That's why I wrote this. This is the guide I wish I had. We'll walk through every single step, from setting up your Meta Business account to handling webhooks, all using Next.js and the robust OAuth method. Let's build something cool.
Prerequisites
Before we dive in, make sure you have a few things ready:
- A Next.js 13+ application set up with the App Router.
- A Facebook/Meta account to manage the business side of things.
- A business or personal phone number that you can dedicate to the WhatsApp Business API.
- A way to expose your local server to the internet. ngrok is my go-to for this.
Our Tech Stack:
- Next.js 13+ (App Router)
- Prisma (for talking to our database, whether it's PostgreSQL, MySQL, etc.)
- Auth.js (for user session management)
Understanding the WhatsApp Cloud API
What's the Big Deal with the Cloud API?
The WhatsApp Cloud API is Meta's way of letting us programmatically send and receive WhatsApp messages without hosting the WhatsApp Business API software on our own servers. It's a game changer compared to the old on premise solution.
Here's why I'm a fan:
- It's (mostly) free to start: You only pay for the conversations you initiate, and there's a generous free tier.
- Meta handles the hosting: No need to mess with Docker containers or worry about server uptime. They handle the infrastructure.
- It's way easier to set up: You don't need to go through a Business Solution Provider (BSP) for simple integrations.
- Built to scale: It's designed to handle a massive volume of messages right out of the box.
OAuth vs. System User Tokens
When it comes to authentication, Meta gives us two main paths. Picking the right one early on will save you a headache later.
OAuth Flow (What we're using):
- User-Friendly: Users connect their own WhatsApp Business Account through a standard OAuth screen. It feels professional and secure.
- Multi Tenant Ready: Perfect for SaaS applications where you have multiple customers or organizations connecting their own accounts.
- Automatic Token Refresh: Access tokens expire, but OAuth provides a way to refresh them programmatically. Set it and (mostly) forget it.
- Best for: SaaS products, applications with multiple users/clients.
System User Token:
- Manual Management: You generate a token manually from the Meta Business Dashboard.
- Single-Tenant Focus: Works well if you're building an internal tool for just one organization (e.g., your own company).
- Manual Refresh Required: The token will expire, and you'll have to go back to the dashboard to generate a new one. This can be a pain to maintain.
- Best for: Internal tools, single purpose integrations.
We're going with the OAuth flow in this guide. It's more scalable and the right choice for building a production-ready application that other people will use.
Pricing
WhatsApp messages are charged per conversation. Check current pricing:
- Official WhatsApp Pricing
- Free tier: 1,000 conversations/month
- Conversations: 24-hour messaging window after user's last message
Facebook App Creation
Step 1: Create a New Facebook App
-
Go to Facebook Developers
-
Click "My Apps" → "Create App"
-
Fill in app details:
- App Name: "My WhatsApp Integration" (or your app name)
- App Contact Email: Your email
- UseCase: Select Other option
- Business Account: Select the business account you created
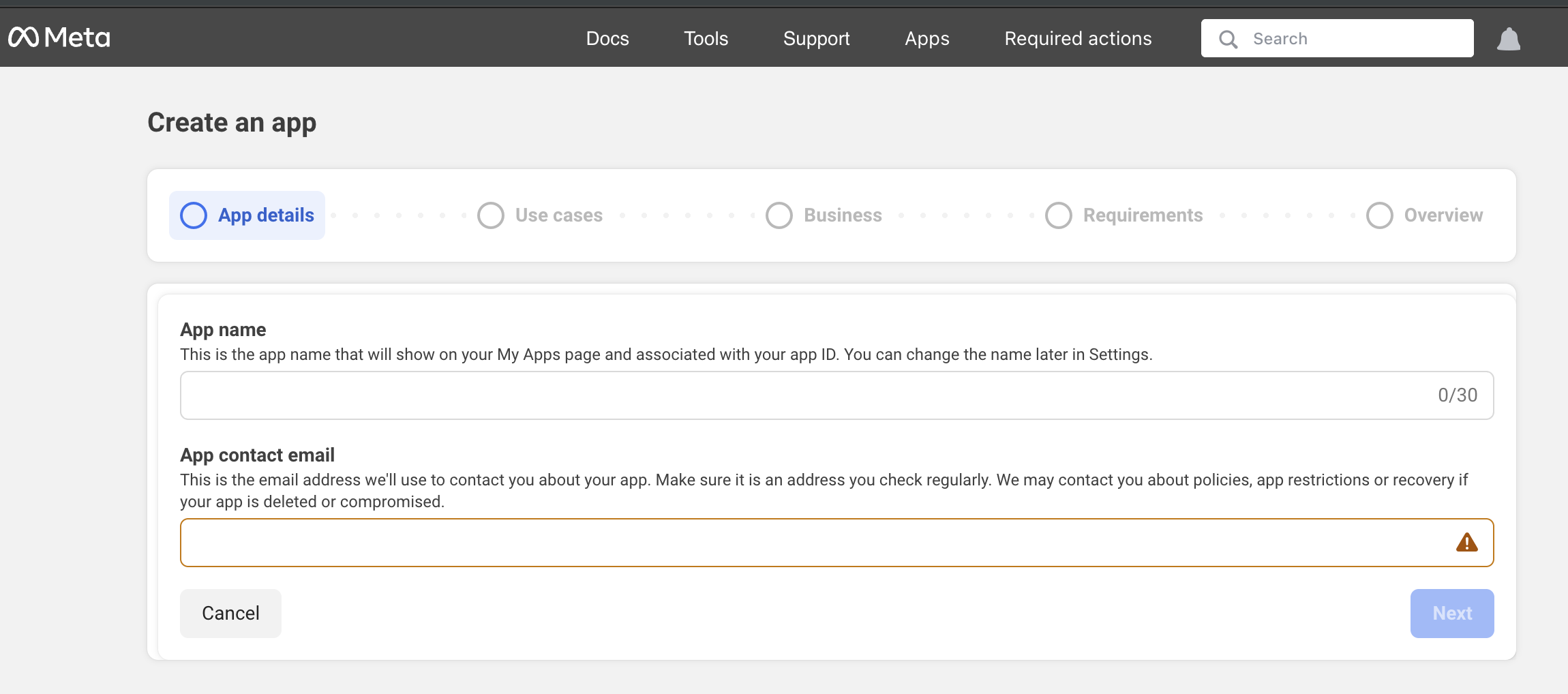
- Click "Create App"
Step 2: Add WhatsApp Product
- In your app dashboard, find "WhatsApp" in the products list
- Click "Set Up"
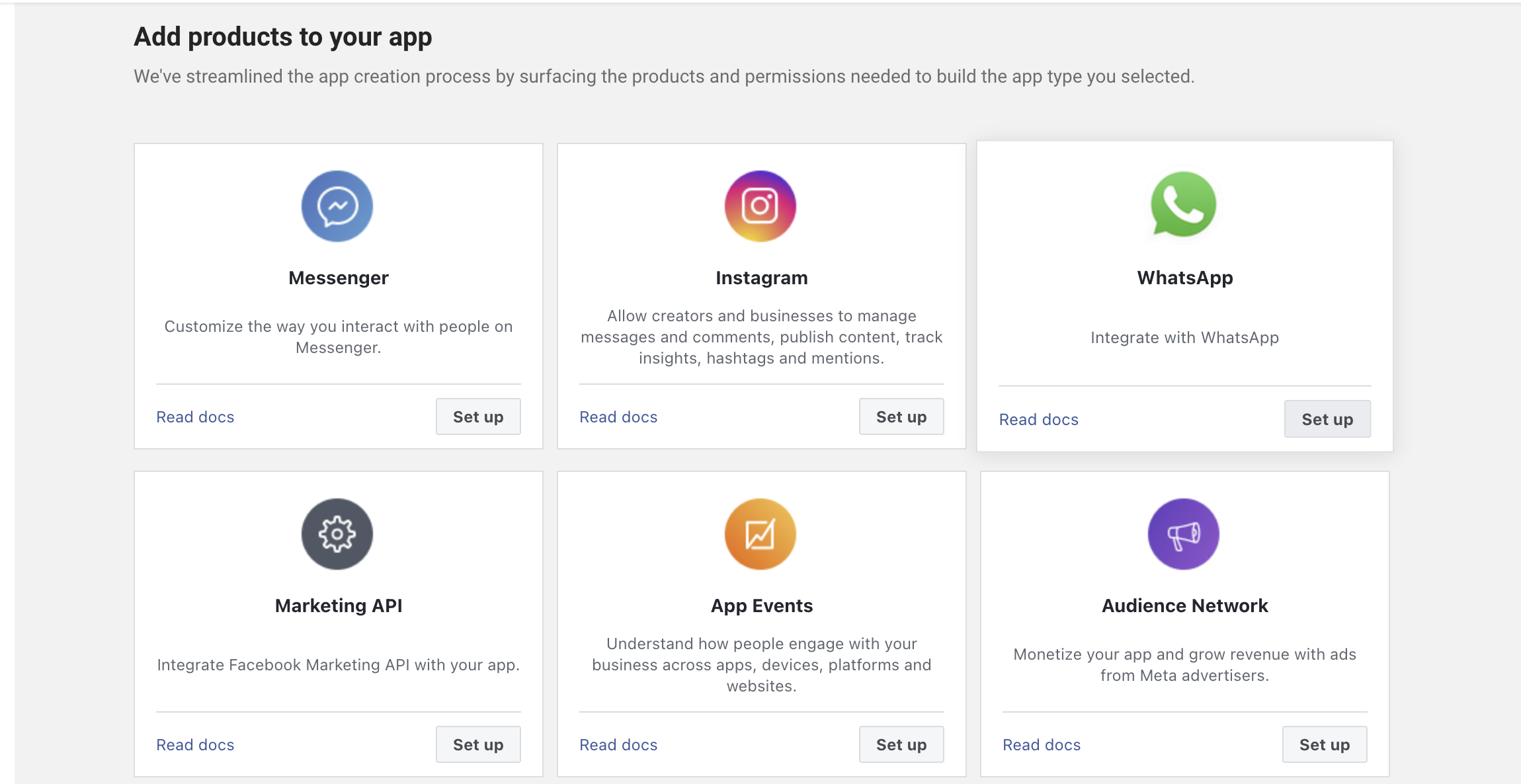
- You'll be redirected to the WhatsApp setup page
Step 3: Configure App Settings
- Go to App Settings → Basic
- Note down these values (you'll need them later):
- App ID
- App Secret (click "Show" to reveal)
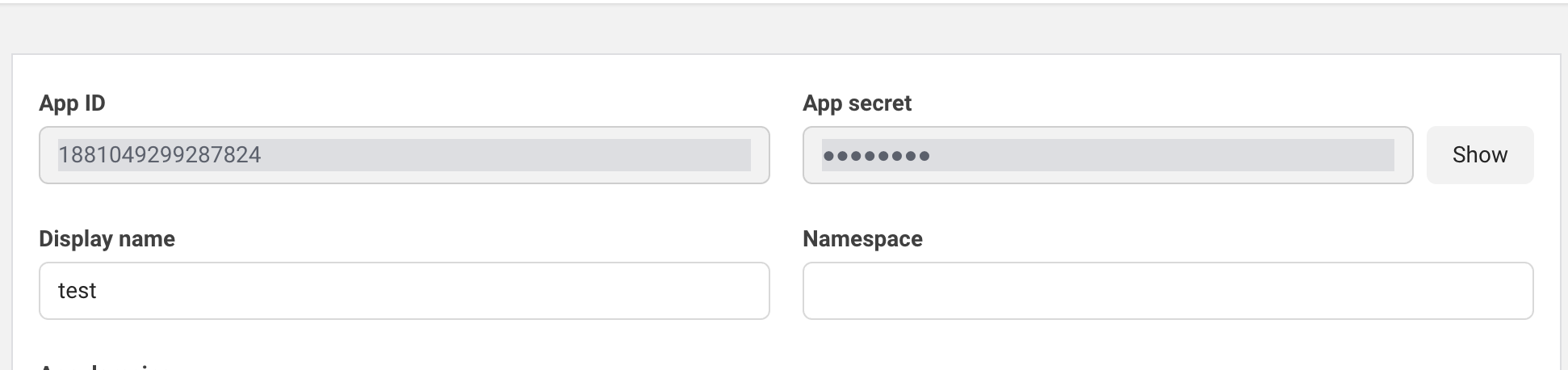
-
Add your app domain:
- App Domains: yourdomain.com
- Privacy Policy URL: https://yourdomain.com/privacy
- Terms of Service URL: https://yourdomain.com/terms
-
Save changes
Step 4: Configure OAuth Settings
- Go to App Settings → Basic
- Scroll to "Add Platform" → Select "Website"
- Enter your Site URL: https://yourdomain.com
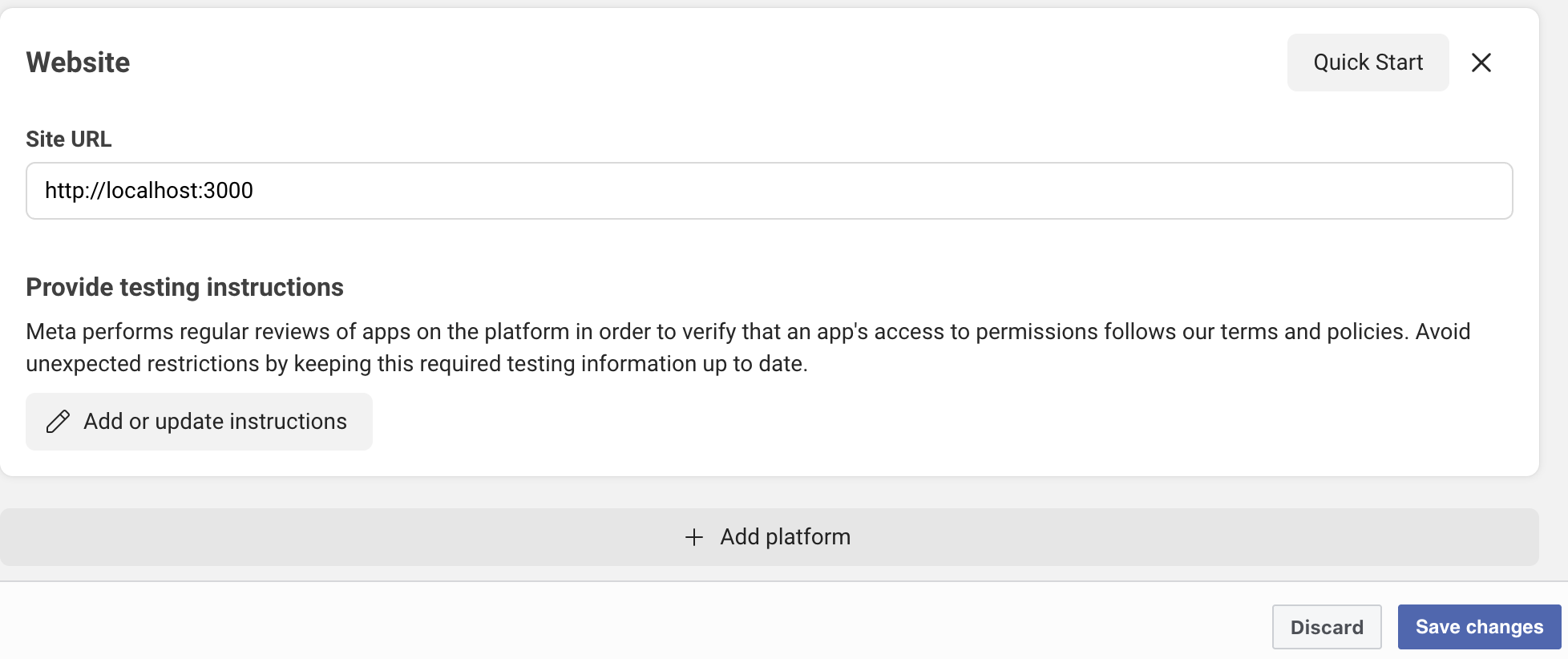
WhatsApp Business Account Setup
Step 1: Create WhatsApp Business Account
- In your app dashboard, go to WhatsApp → Getting Started
- Click "Create a WhatsApp Business Account"
- Select your Business Portfolio (or create a new one)
- Choose "Create a new WhatsApp Business Account"
- Enter your Business Name and Category
- Click "Continue"
Step 2: Add Phone Number
You have two options:
Option A: Use Your Own Number (Recommended for Production)
- Click "Add phone number"
- Enter your business phone number
- Select verification method:
- SMS
- Voice Call
- Enter the 6-digit verification code
Important:
- Once verified, this number can only be used with WhatsApp Business API
- You cannot use the regular WhatsApp app with this number
- Choose wisely - this is permanent!
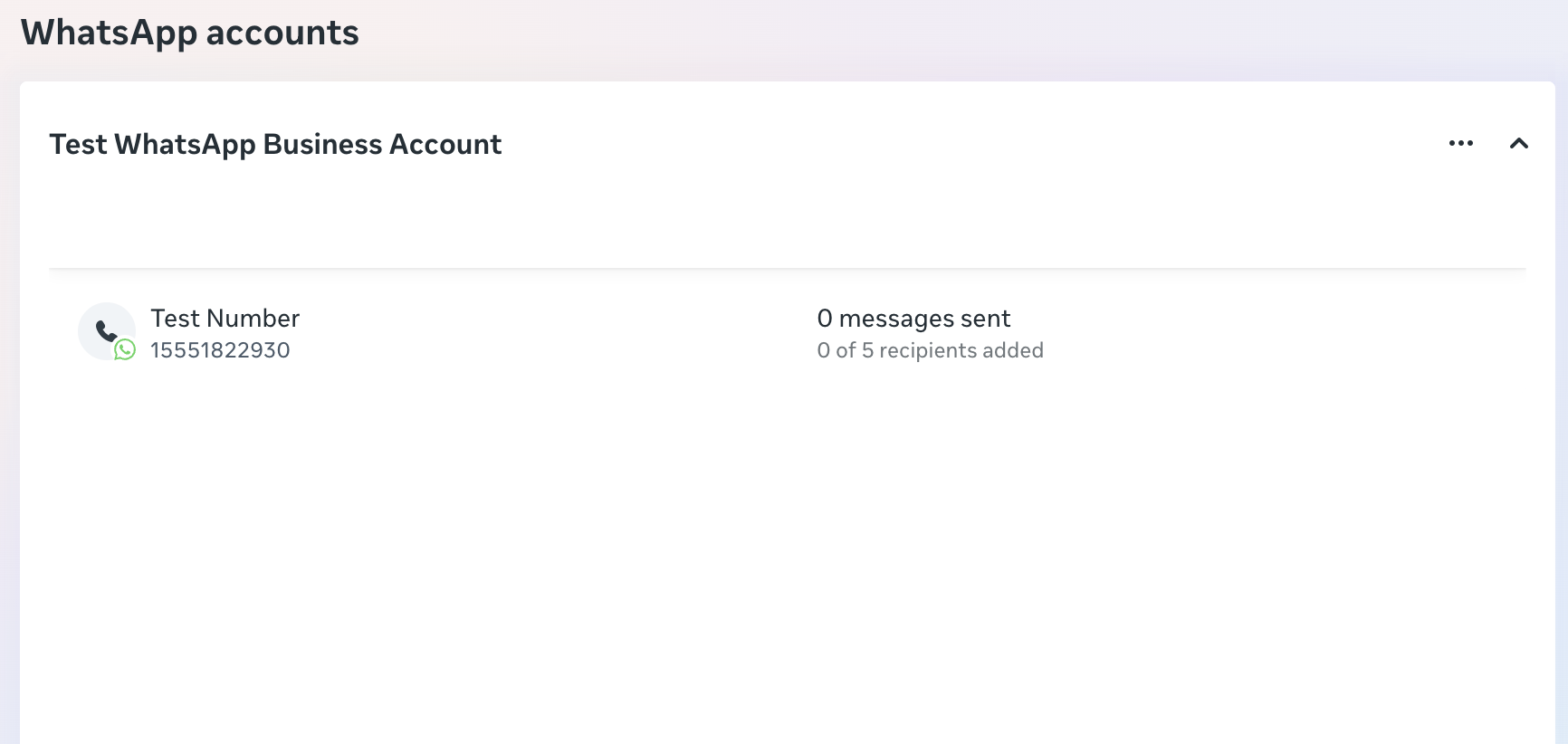
Option B: Use Meta's Test Number (For Development)
- Meta provides a test phone number automatically
- Find it under WhatsApp → Getting Started → Send and receive messages
- Note the Phone Number ID and WABA ID
Test numbers have limitations:
- Can only message 5 verified numbers
- Cannot be used in production
- Perfect for development and testing
Step 3: Get Your Credentials
You need these values for your application:
-
Phone Number ID:
- Go to WhatsApp → Quick Start
- Find "Phone number ID" under your phone number
- Copy this value
-
WhatsApp Business Account ID (WABA ID):
- Found in the same section
- Copy this value
-
Access Token (Temporary):
- In the same section, you'll see a temporary 24 hour token
- This is just for testing - OAuth will generate long-lived tokens
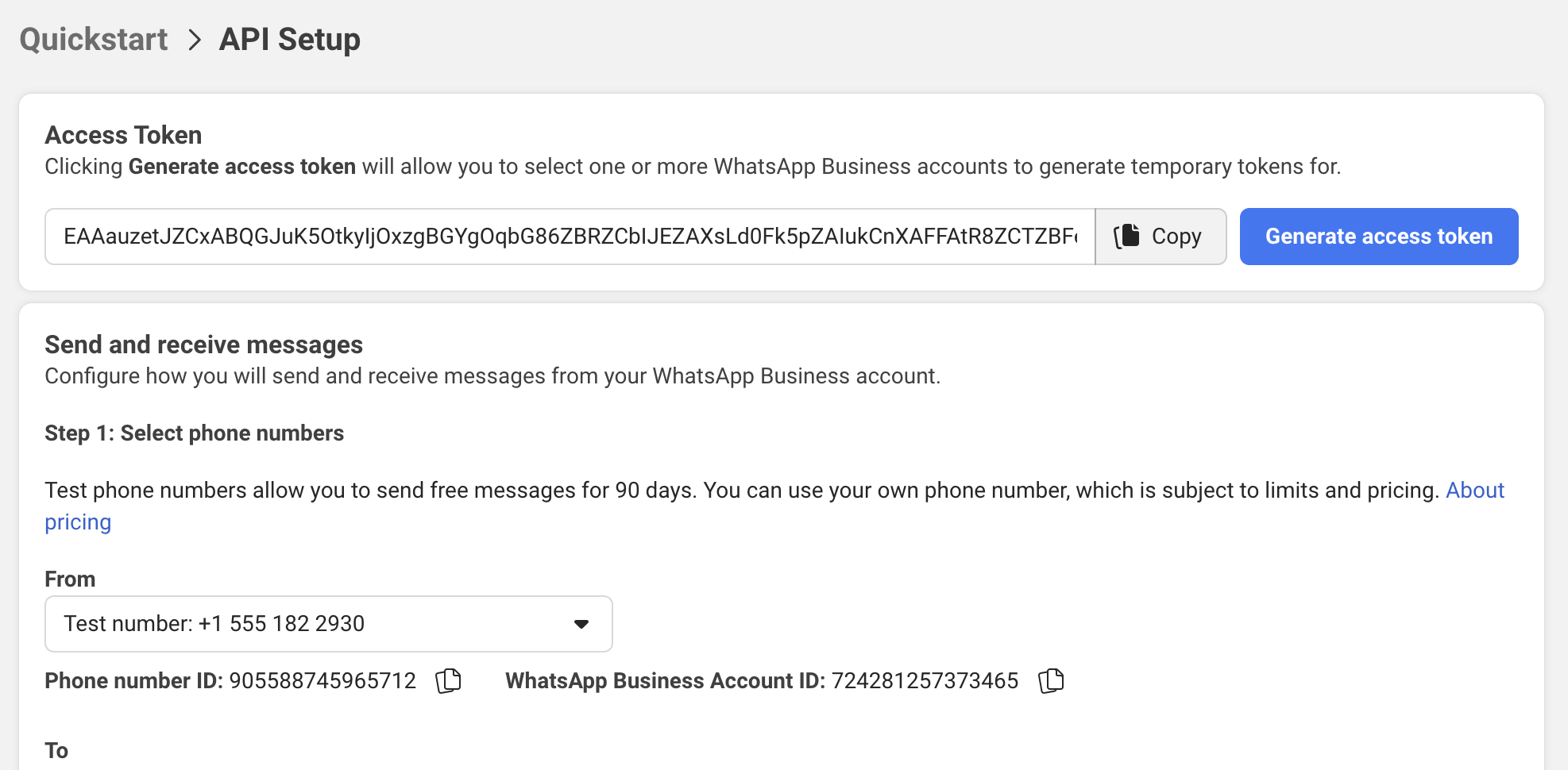
Refer this docs page for more details on these values: WhatsApp Cloud API Overview
Webhook Configuration
Webhooks allow your application to receive incoming messages and status updates in real-time.
Step 1: Understand Webhook Requirements
Meta requires:
- HTTPS endpoint (no HTTP in production)
- Publicly accessible URL (no localhost - use ngrok for dev)
- GET endpoint for webhook verification
- POST endpoint for receiving events
Step 2: Generate Verify Token
Create a random string for webhook verification:
# Generate a random token
openssl rand -base64 32Save this as your WHATSAPP_VERIFY_TOKEN - you'll need it in your code and Meta dashboard.
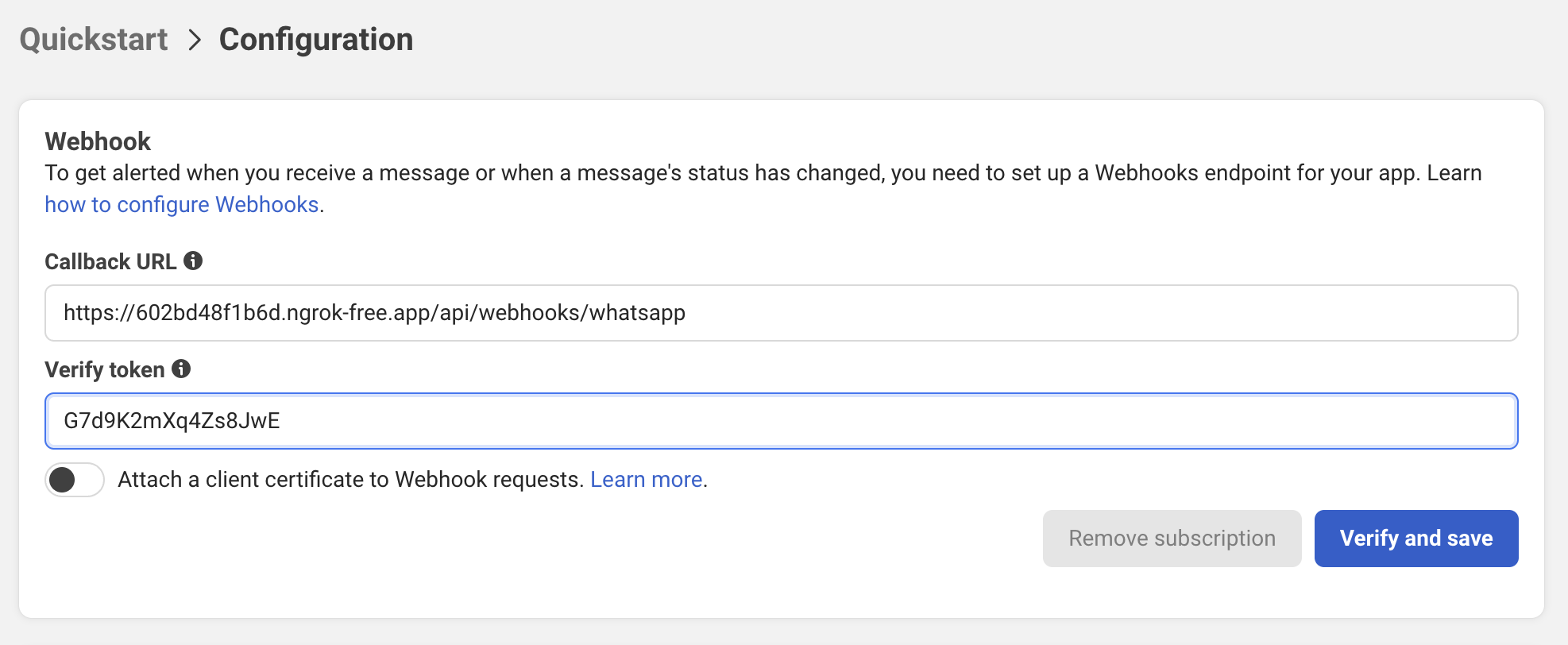
Step 3: Configure Webhook URL in Meta
- Go to WhatsApp → Configuration
- Find "Webhook" section
- Click "Configure"
- Enter your webhook details:
- Callback URL: https://yourdomain.com/api/webhooks/whatsapp
- Verify Token: The token you generated above
- Create a GET endpoint in your Next.js app to handle verification:
// /api/webhooks/whatsapp/route.js
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server';
export const GET = (async (req) => {
try {
const url = new URL(req.url);
const mode = url.searchParams.get("hub.mode");
const verifyToken = url.searchParams.get("hub.verify_token");
const challenge = url.searchParams.get("hub.challenge");
if (mode === "subscribe") {
if (!verifyToken) {
return NextResponse.json({message: "Unauthorized"}, {status: 401});
}
if (!process.env.WHATSAPP_VERIFY_TOKEN) {
return NextResponse.json({message: "WA_VERIFY_TOKEN not configured"}, {status: 500});
}
if (verifyToken === process.env.WHATSAPP_VERIFY_TOKEN) {
console.log("Webhook verified successfully");
return new NextResponse(challenge ?? "", {status: 200});
}
}
return NextResponse.json({message: "Verification failed"}, {status: 403});
} catch (error) {
console.error("Webhook verification error:", error);
return NextResponse.json({message: "Internal server error"}, {status: 500});
}
});
export const POST = (async (req) => {
try {
const body = await req.json();
console.log("Incoming webhook payload:", JSON.stringify(body, null, 2));
// In Part 2, we'll process this payload.
// For now, we'll just acknowledge receipt.
return NextResponse.json({ status: "success" }, { status: 200 });
} catch (error) {
console.error("Webhook POST error:", error);
return NextResponse.json({ message: "Internal server error" }, { status: 500 });
}
});- Click "Verify and Save"
Common Error: If verification fails:
- Ensure your endpoint is publicly accessible
- Check that your GET endpoint returns the challenge correctly
- Verify your token matches exactly
Step 4: Subscribe to Webhook Fields
After verification, subscribe to these events:
-
Check these boxes:
- messages (incoming messages)
-
Click "Subscribe"
Testing with Test Numbers
Before going live, test your integration thoroughly.
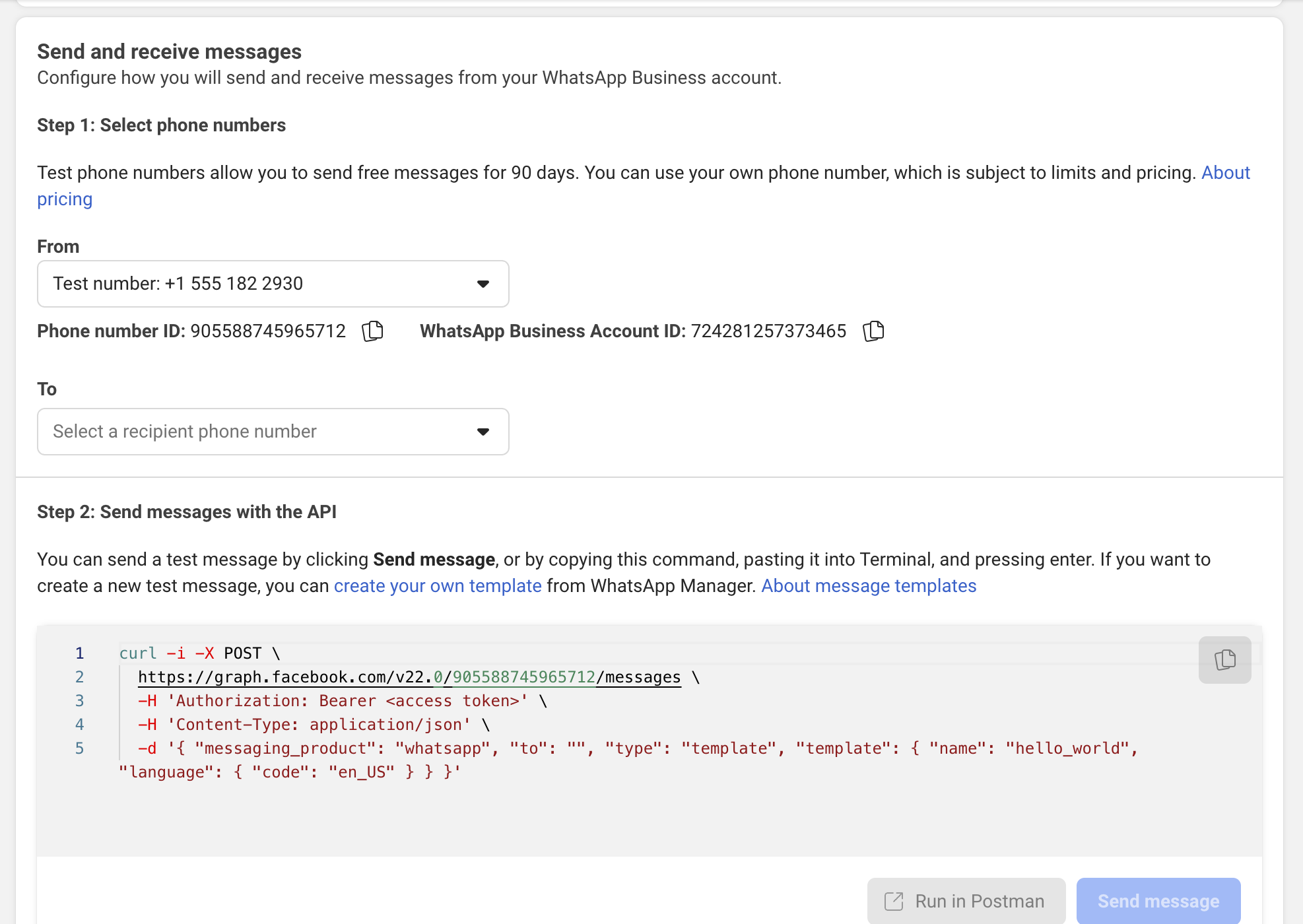
Step 1: Add Test Numbers
- Go to WhatsApp → API Setup
- Find "To" section
- Click "Add phone number"
- Enter a phone number you want to test with
- You'll receive a verification code via WhatsApp
- Enter the code to verify
Limit: Test numbers can only message up to 5 verified recipients
Step 2: Send Your First Test Message
Meta provides a test curl command:
curl -X POST "https://graph.facebook.com/v24.0/YOUR_PHONE_NUMBER_ID/messages" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"to": "RECIPIENT_PHONE_NUMBER",
"type": "text",
"text": {
"body": "Hello from WhatsApp Cloud API!"
}
}'Replace:
YOUR_PHONE_NUMBER_IDwith your Phone Number IDYOUR_ACCESS_TOKENwith the temporary token from MetaRECIPIENT_PHONE_NUMBERwith a verified test number (format:1234567890)
Step 3: Verify Webhook Reception
Once your webhook is verified and subscribed to messages, you need to test that you can receive incoming message notifications. With the POST handler added to our route, your endpoint is now ready to receive these events.
You can trigger a test in two ways:
Option A: Reply from WhatsApp (Manual Test)
- Use the
curlcommand from the "Send Your First Test Message" step to send a message to your verified test number. - Open WhatsApp on that phone and reply to the message.
- Check your Next.js application's console logs. You should see the incoming payload logged by our new
POSThandler.
Option B: Simulate with a curl command (Programmatic Test)
For a faster, more direct test without needing a phone, you can simulate the webhook event that WhatsApp sends. This is perfect for development and automated checks.
Open your terminal and run the following curl command. Make sure to replace https://yourdomain.com with your public URL (e.g., from ngrok) and update the placeholder IDs.
curl -X POST 'https://yourdomain.com/api/webhooks/whatsapp' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"object": "whatsapp_business_account",
"entry": [{
"id": "YOUR_WABA_ID",
"changes": [{
"value": {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"metadata": {
"display_phone_number": "15550001234",
"phone_number_id": "YOUR_PHONE_NUMBER_ID"
},
"contacts": [{
"profile": { "name": "Test User" },
"wa_id": "15551234567"
}],
"messages": [{
"from": "15551234567",
"id": "wamid.TEST_MESSAGE_ID",
"timestamp": "1700000000",
"type": "text",
"text": { "body": "Hello from a test!" }
}]
},
"field": "messages"
}]
}]
}'After running this, check your server logs. Whichever method you choose, you should see the incoming payload logged to your console.
Example webhook payload:
{
"object": "whatsapp_business_account",
"entry": [{
"changes": [{
"value": {
"messaging_product": "whatsapp",
"metadata": {
"phone_number_id": "123456789"
},
"messages": [{
"from": "1234567890",
"id": "wamid.xxx",
"timestamp": "1234567890",
"type": "text",
"text": {
"body": "Hello back!"
}
}]
}
}]
}]
}Part 1 Complete!
You now have:
- Meta Business Account created
- Facebook App with WhatsApp product
- WhatsApp Business Account with phone number
- Webhook configured and verified
- Test numbers added and verified
What's Next?
In Part 2, we'll cover:
- Setting up OAuth flow in Next.js
- Database schema for storing tokens
- Token refresh logic
- Sending messages
- Receiving and processing messages
- Security best practices
- Production deployment checklist
Useful Resources
- WhatsApp Cloud API Documentation
- WhatsApp Business API Pricing
- Meta Business Manager
- Facebook Developer Console
- Webhook Reference
Continue to Part 2: Implementation →